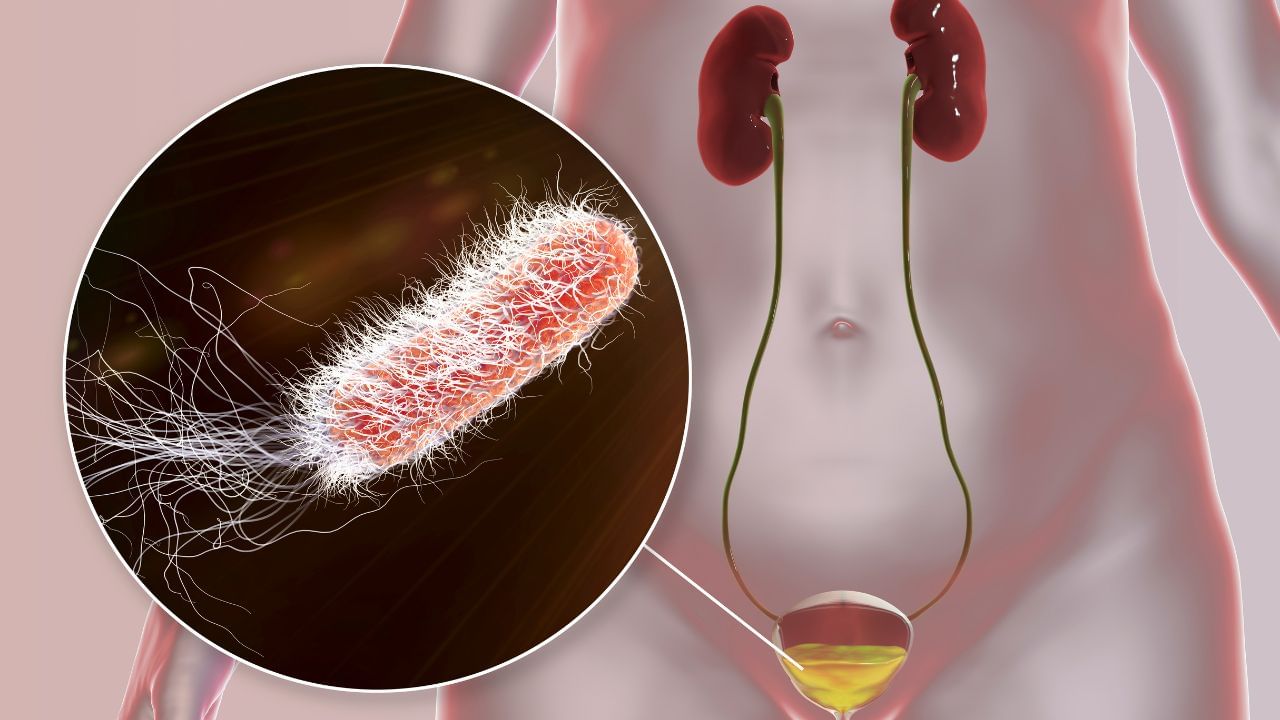
Urine infection in women
Urinary tract infection (UTI) in women is a common but serious health problem. This infection occurs when bacteria (mostly E. Coli)) It reaches the bladder through the urethra and begins to flourish there. Women are small, due to which bacteria reach the bladder quickly. Therefore, the risk of UTI in women is higher than that of men.
Due to urinary tract infection in women
Of women Urethra Would be smaller than men. This is why the bacteria present in the stool, especially E. ColiEasily enter the urinary tube and reach the bladder and spread the infection. Many times women’s cleanliness habits also cause this infection. For example, after using the toilet, cleaning incorrectly, wearing dirty or moist undergarments or keeping urination for a long time. During periods, the use of hygiene and repeated use of public toilet can also increase the risk of urine infection.
Symptoms of urine infection (UTI)
Symptoms of UTI in women may look light, but it can be dangerous to take them lightly. If it is identified and treated in time, then this infection can be cured easily. Cleanliness, drinking adequate water and taking care of toilet hygiene are the most effective ways to prevent uti.
Desire to come again and again
Burning or severe pain while urinating
Urine
Urine
Lower abdominal pain or pressure
Tiredness and mild fever
If the infection starts spreading up to the kidney upwards from the bladder, then fever, chills and tiredness can also be felt. Therefore, it is important that women take full care of their hygiene, drink enough water throughout the day, never stop urination and ignore any symptoms.
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
If the symptoms mentioned above remain for more than 1-2 days, or blood in the urine, fever, or back pain-contact the doctor immediately. UTI can reach the kidney if not treated at the right time, which can create a serious condition.