What is tomato fever?Image Credit Source: Getty Images
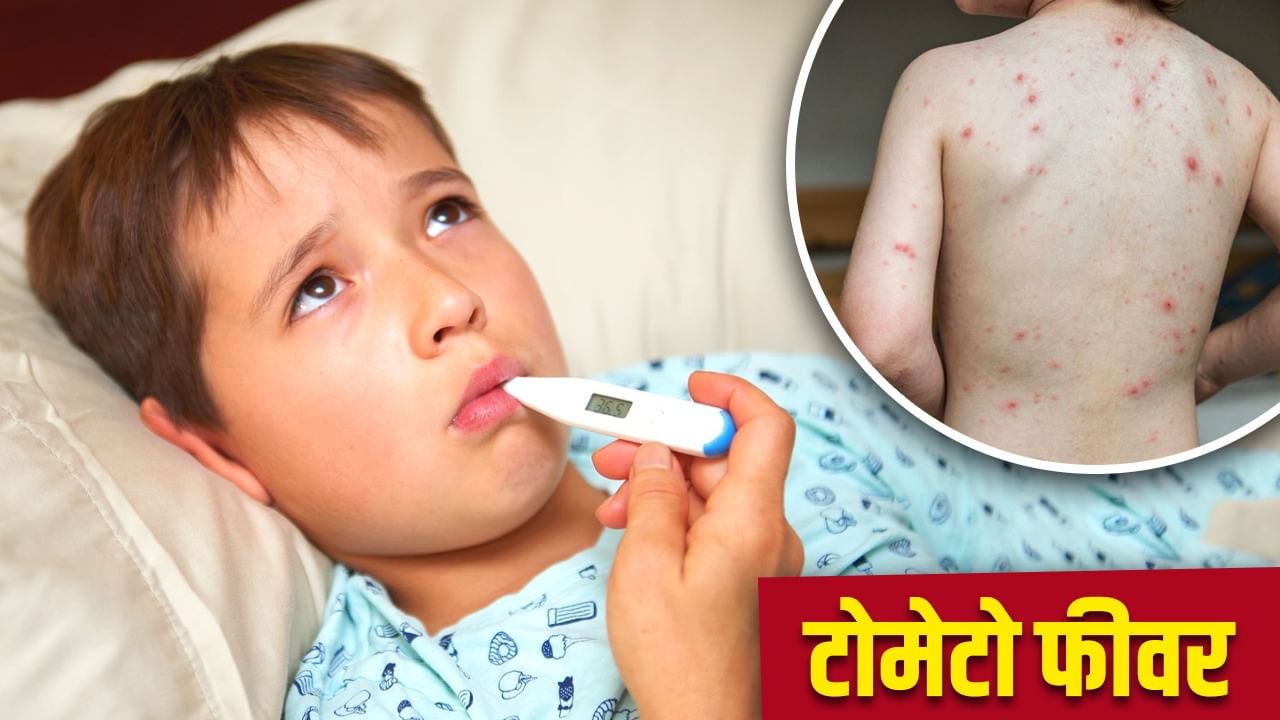
Tomato Fever: Tomato fever is a rare viral infection, which most affects young children. It got such a name because it has red and round blisters on the body, which look like tomatoes. This disease is often found in children under 5 years of age. Its risk increases in the rainy season because at this time there is more moisture and dirt in the atmosphere, due to which mosquitoes and viruses spread rapidly. During the rain, the immunity of children also becomes weak, due to which they are more victims of infection. In school or playgroup, children dissolve and share toys, food and drink also promotes infection. That is why it is very important to be cautious about this disease during rainy days.
Dr. Vipin Chandra Upadhyay in Pediatric Department at Ghaziabad District Hospital It is said that tomato fever can affect the body of children in many ways. First of all it reduces children’s energy, which makes them feel tired and weak. Red blisters on the body cause severe irritation and itching, which can make the child restless. In many cases, these blisters also fall on the mouth and tongue, which makes children difficult to eat and drink. Constant fever and dehydration can cause problems like dizziness, headache and vomiting. If there is no timely treatment, then this infection further weakens the immunity of children. This is the reason why doctors advise not to ignore the initial symptoms and conduct an immediate examination, so that it does not have a serious effect on the children’s body.
What are the symptoms of tomato fever?
Dr. Rakesh Bagdi of Pediatric Department in AIIMS It is said that early symptoms of tomato fever may look like colds or viral fever, but gradually it starts giving different identity. The most prominent symptom is high fever, which can often reach 101–103 degrees. Along with this, small red blisters or blisters start coming out on the body. These blisters especially appear more around hands, feet and mouth. Children also feel loss of appetite, persistent fatigue, irritability and weakness.
Many times problems like severe pain in the body, stiffness in joints and sore throat also arise. The infected child may have problems with dehydration because problems like vomiting and diarrhea are also seen. This disease is contagious and can easily spread from one child to another, so timely identification and caution is very important.
How to rescue?
Pay special attention to children’s cleanliness.
In case of fever or blisters, see the child immediately to the doctor.
Keep the infected child separate from other children.
Keep children away from dirty water and infected things.
Give children nutritious diet and adequate water so that the immunity of the body increases.
Avoid sharing children’s goods in school and playgroup.